Understanding Complex Trauma Injuries: Types, Treatment, and Recovery
Introduction
Complex trauma injuries can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life, requiring specialized care and treatment. In this article, we’ll explore the nature of complex trauma injuries, the treatment options available, and the road to recovery for those affected by such injuries.
What are Complex Trauma Injuries?
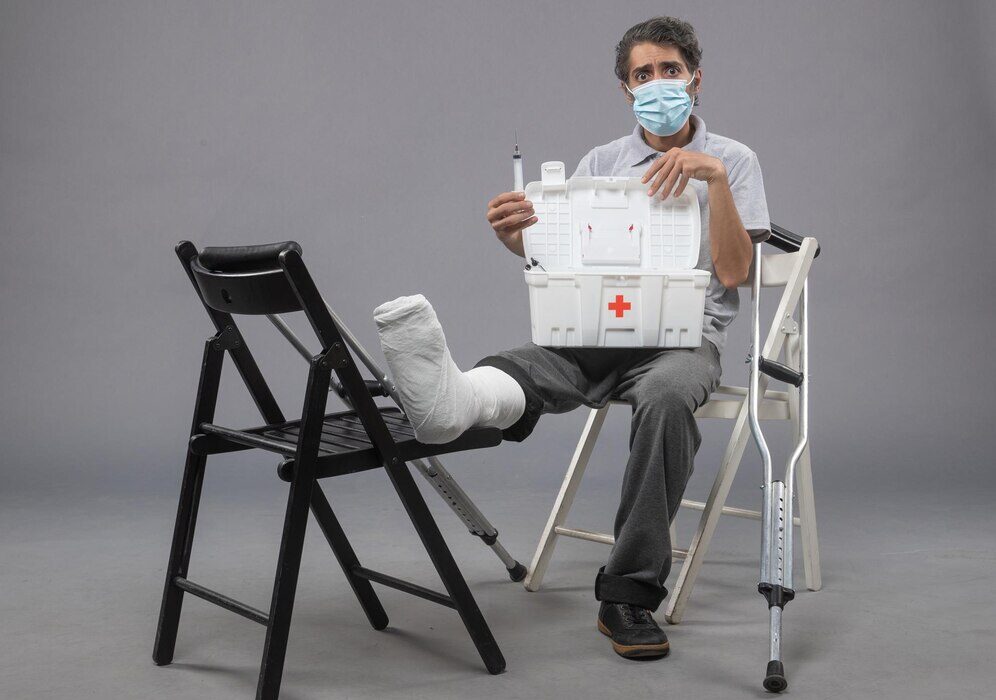
Complex trauma injuries refer to severe and often multiple injuries that affect different parts of the body simultaneously. These injuries typically involve damage to bones, joints, soft tissues, and organs, presenting a challenging scenario for both patients and healthcare providers.

Common Types of Complex Trauma Injuries
Complex trauma injuries can include:
- Multiple Fractures: Involving more than one bone and often requiring surgical intervention.
- Polytrauma: Injuries affecting multiple body systems, such as the musculoskeletal, neurological, and vascular systems.
- Crush Injuries: Resulting from compression of body tissues, often leading to severe damage.
- Penetrating Injuries: Caused by objects entering the body, potentially causing extensive internal damage.

Treatment Approaches for Complex Trauma Injuries
The management of complex trauma injuries typically involves a multidisciplinary approach, including:
- Emergency Stabilization: Prioritizing the stabilization of vital functions and addressing life-threatening injuries.
- Surgical Intervention: Complex fractures, soft tissue damage, and internal injuries may require surgical repair and reconstruction.
- Rehabilitation: Physical therapy and occupational therapy play a crucial role in restoring function and mobility post-injury.
- Psychological Support: Coping with the emotional and mental impact of complex trauma injuries is an essential aspect of recovery.

Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery from complex trauma injuries is a gradual process that may involve:
- Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises to improve strength, range of motion, and functional abilities.
- Occupational Therapy: Learning adaptive techniques to perform daily tasks and regain independence.
- Pain Management: Addressing pain through medication, physical modalities, and therapeutic interventions.
- Long-Term Follow-Up: Monitoring for complications, assessing progress, and adjusting the treatment plan as needed.
Conclusion
Navigating the challenges of complex trauma injuries requires a comprehensive and coordinated approach involving healthcare professionals, patients, and their support network. By understanding the nature of these injuries, exploring treatment options, and committing to the recovery process, individuals can work towards regaining function and improving their quality of life post-injury.

 Call Now
Call Now
 Send Reports
Send Reports